2. June 2015 07:50 by Christian in
The battery capacity is essential in EV autonomy. Depending on the automotive OEM a fully charged EV battery can provide between 20 KWh (160 km for Nissan) and 85 KWh (480 Km for Tesla).
Charging Time / 100 Km
| Power Supply
| Voltage
| Max Current
|
6-8 hours
| Single phase - 3.3 kW
| 230 VAC
| 16 A
|
2-3 hours
| Three phase - 10 kW
| 400 VAC
| 16 A
|
3-4 hours
| Single phase - 7 kW
| 230 VAC
| 32 A
|
1-2 hours
| Three phase - 22 kW
| 400 VAC
| 32 A
|
20-30 minutes
| Three phase - 43 kW
| 400 VAC
| 63 A
|
20-30 minutes
| Direct current - 50 kW
| 400 - 500 VDC
| 100 - 125 A
|
10 minutes
| Direct current - 120 kW
| 300 - 500 VDC
| 300 - 350 A
|
Besides charging stations connected to the electrical grid based on fossil-fuel or nuclear power the industry is looking as well into renewable electricity for charging stations like:
- Solar Power Automotive Recharging Station
- E-Move Charging Station
- Wind Powered Charging Station
1. June 2015 19:52 by Christian in
Standards ensure the safety and reliability supporting government policies and legislation. Standards are opening up markets, ensuring interoperability, encouraging innovation and awareness of technical developments and initiatives.
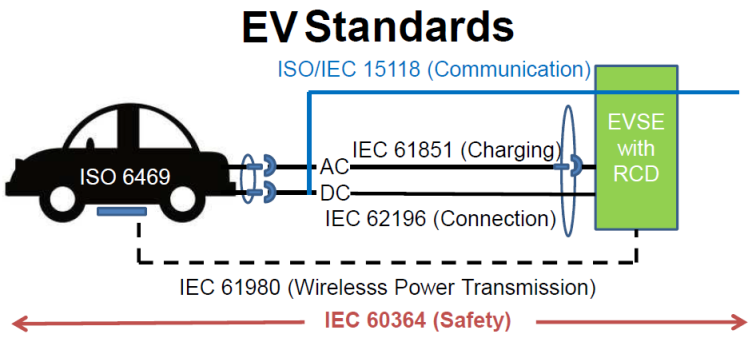
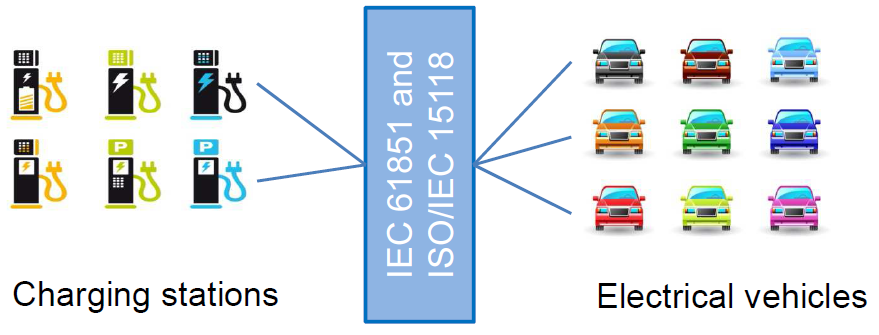
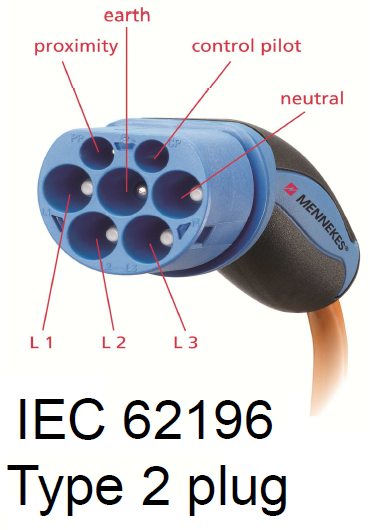
EV_STD_RoadMap_1.pdf (657.24 kb)
1. June 2015 19:10 by Christian in
EV components responsible for electromagnetic emissions are the electric motor, the power converter, the power supply, and the lines/cables connecting them. The high speed switching device part of the power converter is the main source of EMI. The impedance of the electric motor that varies as a function of frequency is also an important factor in EMI analysis. Another EMI contributor is the behavior within the high frequency range of the traction battery providing power to the converter. The high-voltage bus (e.g. 900 V) connecting the power converter with the motor and the power supply must be kept very short to limit the emission of noise. The high-voltage system must be insulated and does not use the car body as return conductor like the low-voltage supply system does. The crosstalk between the different lines and the EMI radiated from the high-voltage cables into EV must be addressed.