There
are several CAN physical layer and other standards:
•ISO 11898-1: CAN Data Link Layer and Physical Signaling
•ISO 11898-2: CAN High-Speed Medium Access Unit
ISO
11898-2 uses a two-wire balanced signaling scheme. It is the most used physical
layer in car
Powertrain
applications and industrial control networks.
•ISO 11898-3: CAN Low-Speed, Fault-Tolerant, Medium-Dependent Interface
•ISO 11898-4: CAN Time-Triggered Communication
ISO
11898-4 standard defines the time-triggered communication on CAN (TTCAN). It is
based on the
CAN
data link layer protocol providing a system clock for the scheduling of
messages.
•ISO 11898-5: CAN High-Speed Medium Access Unit with Low-Power Mode
•ISO 11898-6: CAN High-speed medium access unit with selective wake-up
functionality
•ISO 11992-1: CAN fault-tolerant for truck/trailer communication
•ISO 11783-2: 250 kbit/s, Agricultural Standard
ISO
11783-2 uses four unshielded twisted wires; two for CAN and two for terminating
bias circuit
(TBC)
power and ground. This bus is used on agricultural tractors. This bus is
intended to provide
interconnectivity
with any implementation adhering to the standard.
•ISO 15765-2 also called ISO-TP, is a standard for flow control and handling of
messages larger than eight bytes.
•SAE J1939-11: 250 Kbit/s, Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)
•SAE J1939-15: 250 Kbit/s, Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) (reduced layer)
The
SAE J1939 standard uses a two-wire twisted pair, −11 has a shield around the
pair while −15 does not. SAE 1939 defines also application data and is widely
used in heavy-duty (truck) and autobus industry as well as in agricultural
& construction equipment.
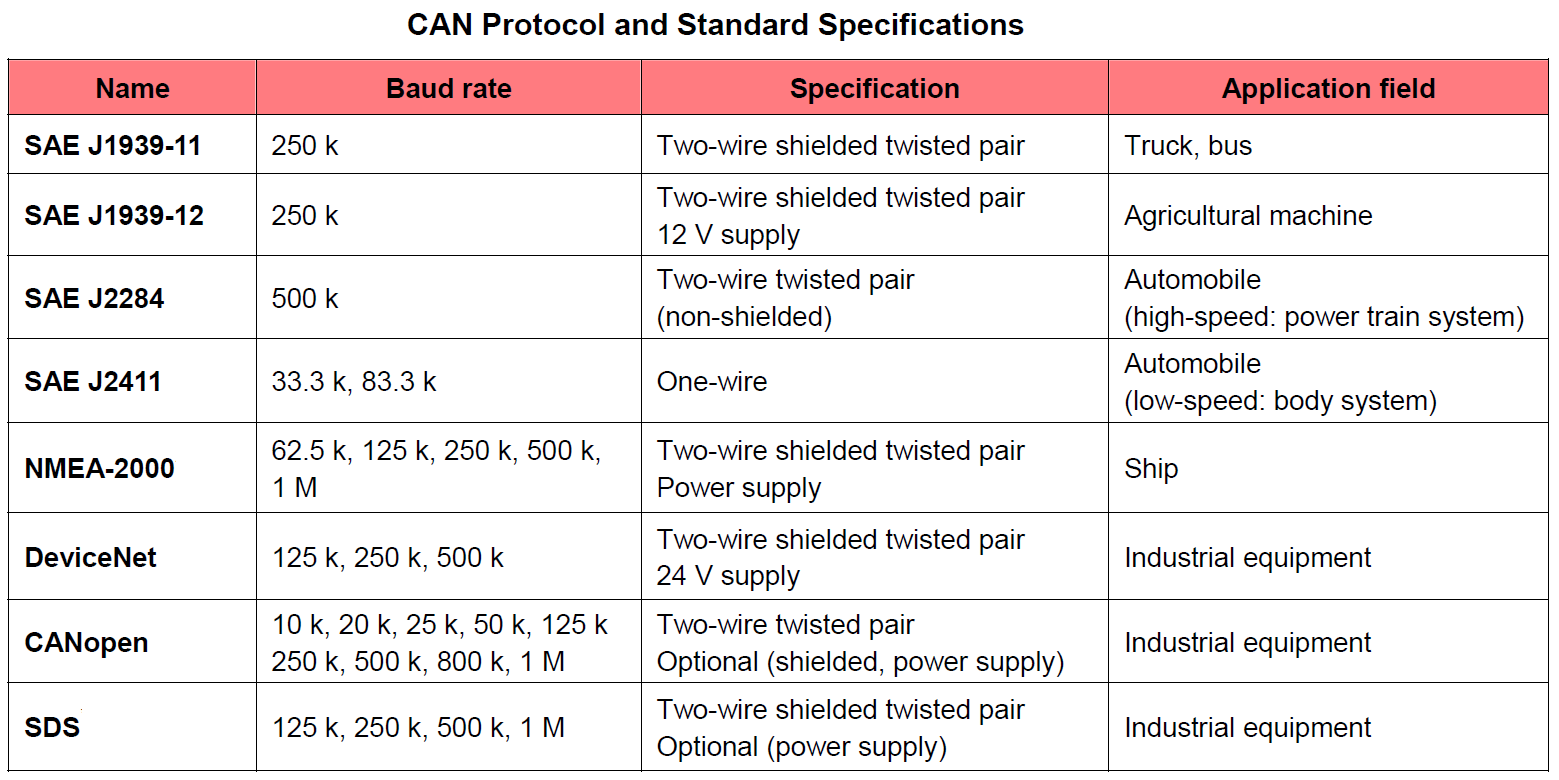
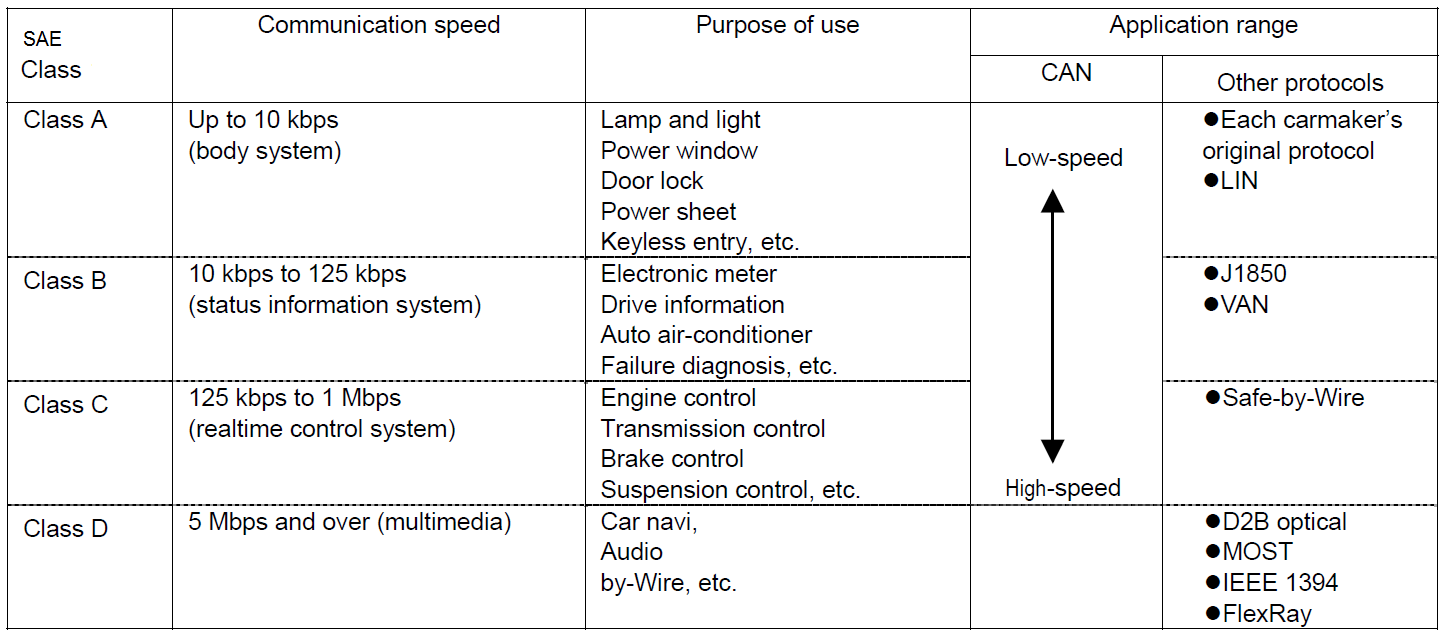
SAE = Society of Automotive Engineers; NMEA = National Marine Educators Association; SDS = Smart Distributed System