30. July 2015 07:39 by streng in
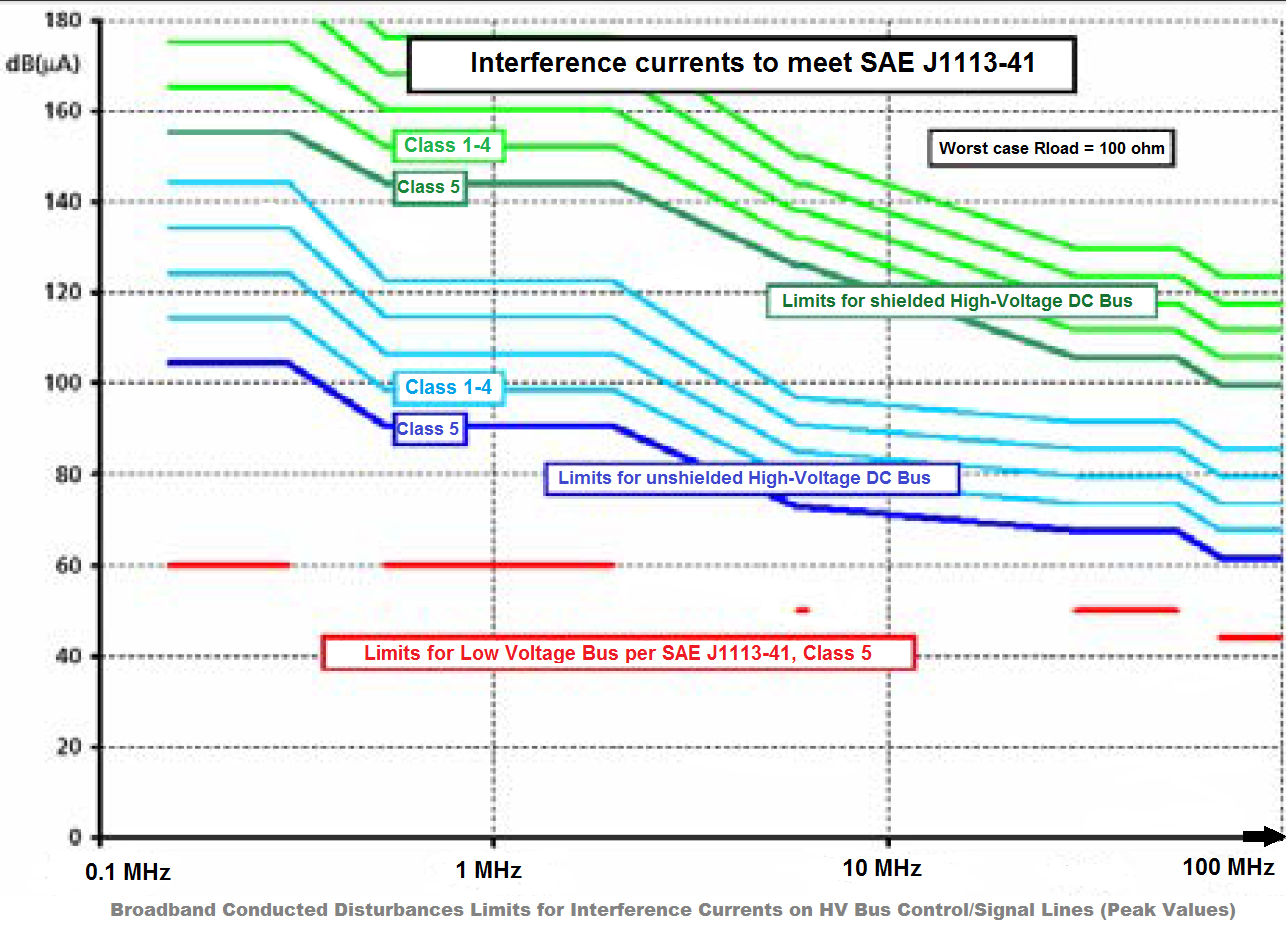
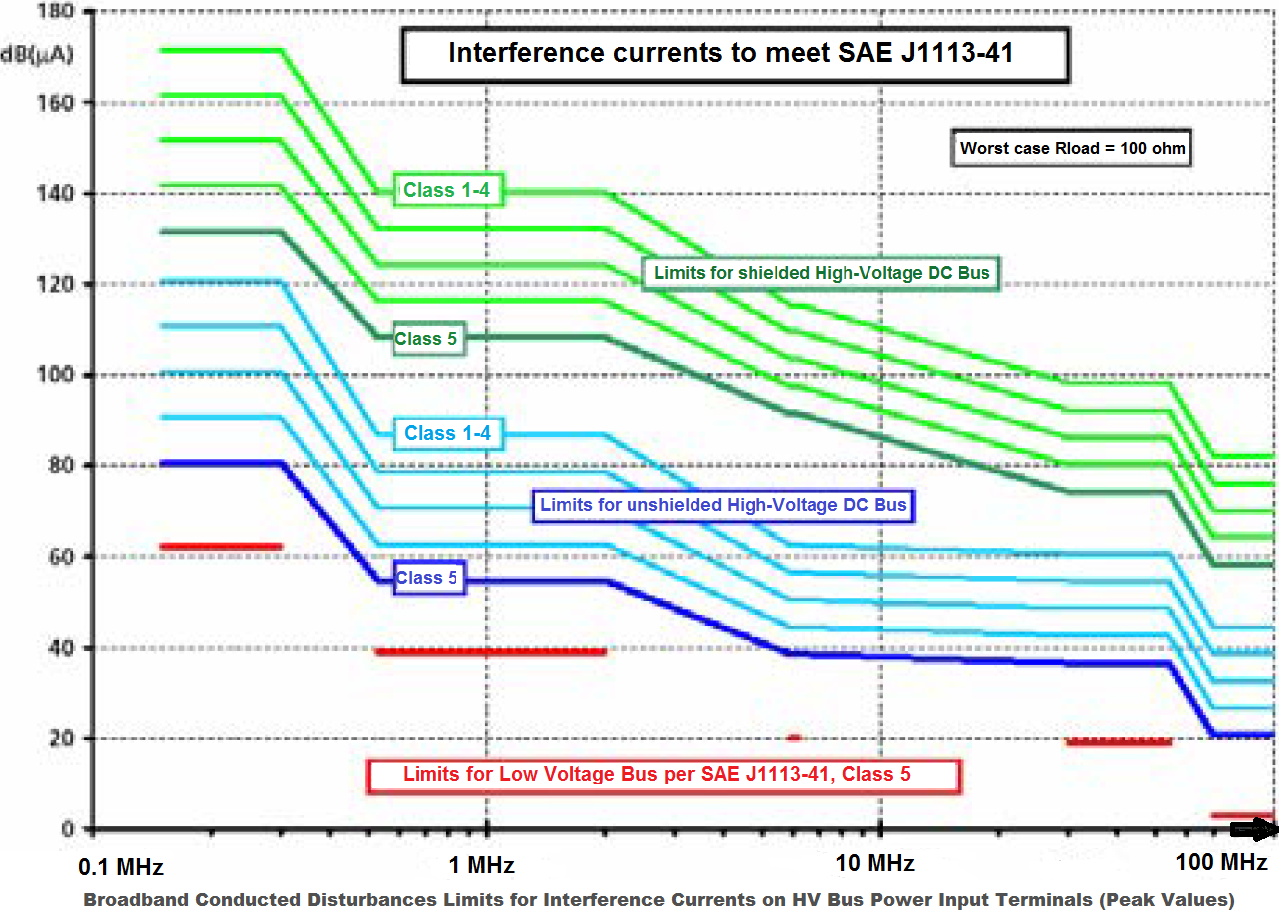
EV require higher power for the electric drive components and higher voltage (900 V) in the high voltage bus. The HV Bus is built as a completely insulated power supply network with cables most often shielded.
The main components of the automotive electric drive are:
- electric motor (the connection between converter and motor must be very short)
- power converter (the main source of EMI due to high speed switching devices with changing pulse patterns)
- power supply (traction battery providing power to the converter is a main part of the path for EMI)
- lines connecting the above components
Each of these components acts as a path for electromagnetic emissions:
- RF noise emissions due to the ratio between the size of the power converter and the frequency of the EMI.
- The high-voltage system is insulated and does not use the car body as return conductor like the low-voltage supply system. However, the high-voltage and the low voltage cables are arranged closely to each other, one important coupling path being the crosstalk between the different lines.
- The drive system can be either noise source or part of the coupling path within EV electrical system.
21. July 2015 22:39 by Christian in
Human Model at the worst radiation point during slow EV charging.
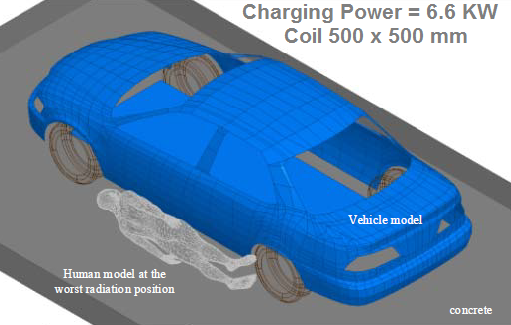
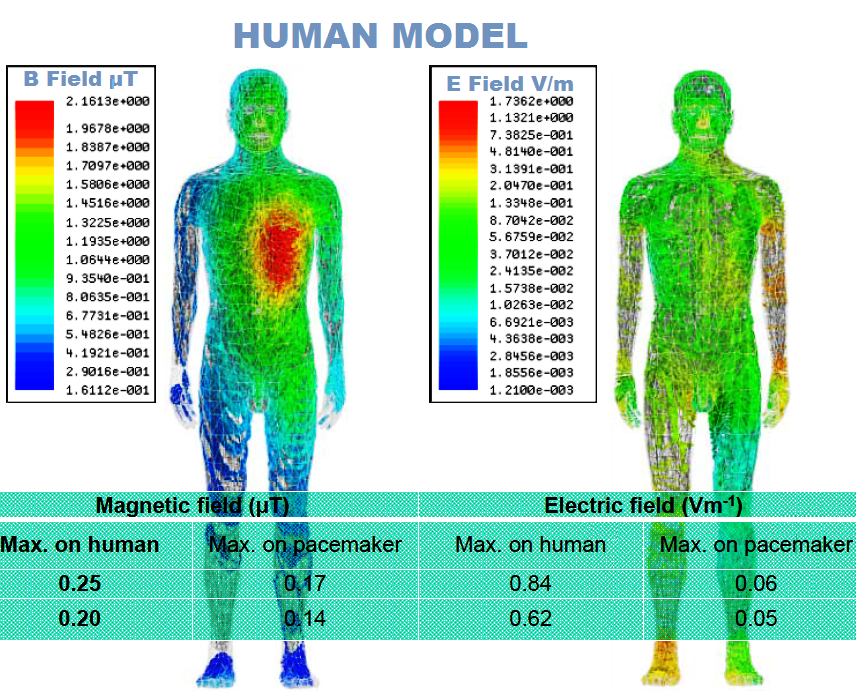
Sources: University of Michigan-Dearborn
21. July 2015 22:01 by Christian in
EV Charging Time & Power Requirement |
Range | 5
minutes | 15
minutes | 30
minutes | 8
hours |
100 miles | 390 kW | 130kW | 65kW | 4 kW |
400 miles | 1560 kW | 520 kW | 260 kW | 16 kW |
Fast
charging shortcomings:
- it
may compromise battery life
- increased
cost for the charging stations
- power
grid heavy loading