How Electromagnetic Fields are propagated and coupled together.
Conductive coupling is usually low frequency noise traveling along a pair of wires due to a common resistive path, which form a loop. Breaking the connection stops the interference (“ground loops”).
Radiated coupling represent EM waves propagating through space from one point to another, whose coupling factor reduces by a factor of 1/r.
Inductive and Capacitive couplig refers to near field effects, which are reduced rapidly with separation (near field terms of 1/r^2 and 1/r^3).
Inductive coupling requires two "loops" coupled together, with the field of the one inducing noise into the other (think transformer).
Example: one cable inducing noise into an adjacent cable.
Inductive coupling is a high di/dt phenomenon.
Capacitive coupling requires two “plates” with the noisy plate inducing a voltage change in the other due to dispersion effects (think capacitor).
Example: heat sink from a switched mode power supply inducing voltage changes in a nearby cable or chassis.
Capacitive coupling is generally a high dv/dt phenomenon.
14. August 2015 05:17 by Christian in
EMC/EMI, Shielding Types of Electromagnetic Coupling: Conducted, Radiation, Magnetic Field, Electric Filed
Electric Field Coupling
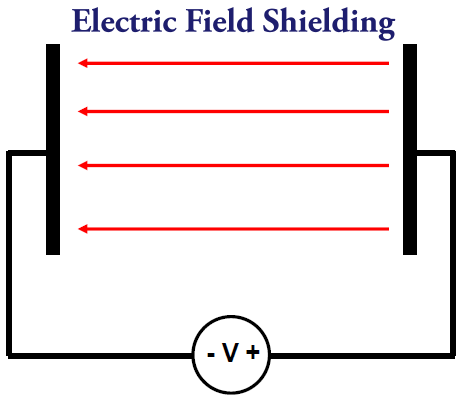
The EF lines start on positive charge and end on negative charge from higher voltage conductors to lower voltage conductors. Any two conductors at different potentials (voltages) have electric field lines between them. EF shields are connected to “ground” to maximize their effectiveness.
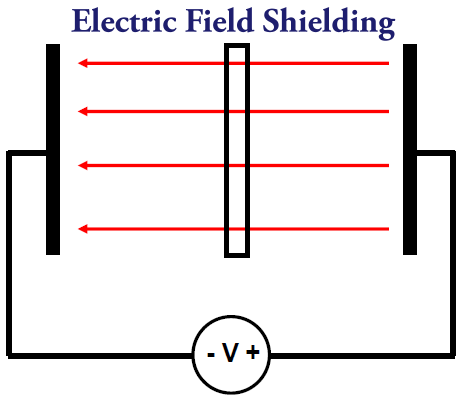
The electric field lines are passing through ungrounded metallic planes.
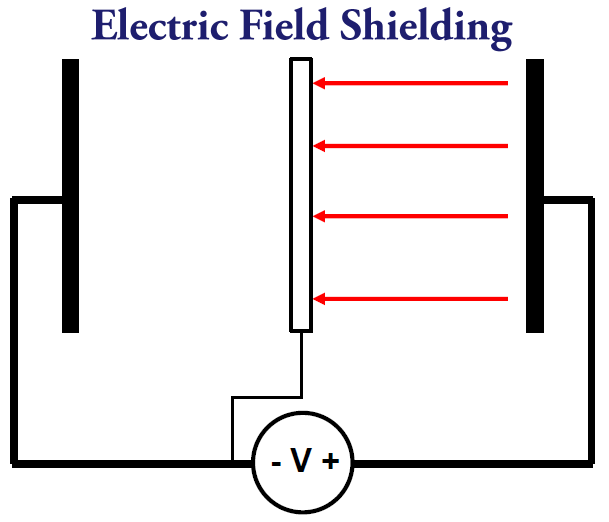
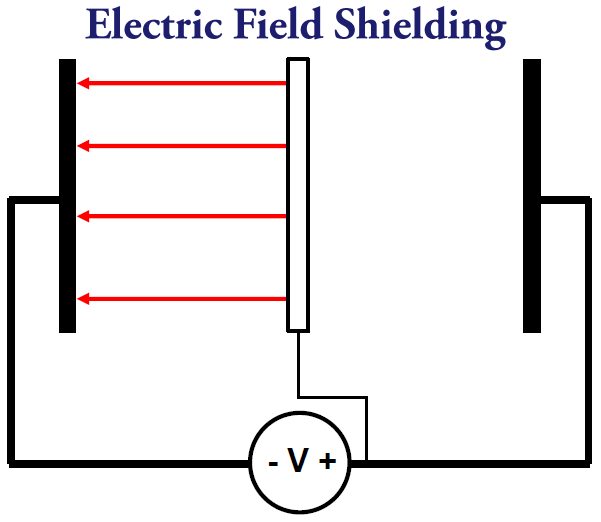
Grounding a copper enclosure does not increase or decrease its shielding property but it reduces the crosstalk within the product itself. The ungrounded shield allows coupling signals from circuits within the shielded enclosure. If the device is connected via external cable to another module the ungrounded shield can serve to capacitively couple signals from outside the enclosure.